Research
Research
- Planning and Coordination Division
- General Services Division
- Technology Services Division
- Dept. of Agricultural Environment
- Dept. of Agricultural Biology
- Dept. of Agro-food Safety and Crop Protection
- Dept. of Agricultural Engineering
- Dept. of Agricultural Biotechnology
- National Agrobiodiversity Center
- Research Paper
Dept. of Agricultural Biotechnology(농업생명자원부)
The Department of Agricultural Biotechnology is a leading national research and development institution to develop domestic agricultural biotechnology with state-of-the-art facilities for modern biotechnology. The department's national mission is to establish a national R&D infrastructure for agricultural biotechnology and biotechnology research in order to create a new growth engine for future agriculture in the era of bio-economics. This department focuses on cutting-edge research to improve the productivity and value of agriculture by overcoming technological limitations. The department consists of four divisions: Genomics, Metabolic Engineering, Gene Engineering, and Biosafety.
(1) Genomics Division
Function
- Assembly and annotation of the genomes of agricultural crops
- Discovery of useful genes and development of molecular markers for crop improvement
- Establishment of infrastructure for analyzing agricultural big data
- Leading agricultural data center, integrating and offering advanced analysis of big data for academia, research, and industry.
Major Achievements
- Genome sequencing of agricultural organisms (27 plants, 7 animals, and 6 insects)
- Carried out the National Agricultural Genome Program (NAGP) - Established the National Agricultural Biotechnology Information Center (NABIC)
- Completed the National Agricultural Genome Program (NAGP)
- Genome assembly and annotation of 27 plants, 7 animals, 6 insects (2014 ~ 2021)

- Establishment of the National Agricultural Biotechnology Information Center (NABIC)
- Roles (2002 ~)
- - Bioinformatics service for the agricultural biotechnology research
- - Integration and management of national agricultural omics big-data
- System infrastructure and service platform
- - System infrastructure: 12 servers, 1.6 PB storage, 50 bioinformatics S/W
∙ NABIS(High Performance Computer) : CPU 11,040 cores, 14.7 TB memory
∙ NABIS2(High Performance Computer) : CPU 69,696 cores, 372 TB memory - - Public data : 5,352,748 records, 54.72 TB (~2023.9)
- - System infrastructure: 12 servers, 1.6 PB storage, 50 bioinformatics S/W
- Roles (2002 ~)
- Launch of the Agricultural Biotechnology Supercomputing Center with a High-Performance-Computer (HPC) system ranked 339th in the world (June 2023)

(2) Metabolic Engineering Division
Function
- Investigation of natural product biosynthesis pathways through plant metabolomics and production of high-value materials through plant metabolic engineering/synthetic biology
- Production of biopharmaceutical protein using plant molecular farming systems
- Improvement of agricultural practices using environment control and metabolomics
- Metabolomics research based on agricultural bioresources
- Production of high value-added and functional materials using agro-biotechnology
- Biopharmaceutical protein production through molecular farming
Major Achievements
- Identified allergy-causing genes through analysis of wheat varieties (named “Ofree”) with reduced allergies.
- novel wheat mutant without four allergen gluten proteins - Flower color modification through metabolic engineering
- Flavonoids: chalcones, aurones, flavones, flavonols, anthocyanins - Production of γ-linolenic acid and stearidonic acid in perilla seeds
- Production of biopharmaceutical protein from alfalfa, rice, and hairy roots
- tissue Plasminogen Activator (t-PA): prevents the formation of blood clots - Extension of fruit shelf life and promotion of plant growth using sound waves
- Development of wheat variety ‘Ofree’ with reduced gluten allergen
- Enhanced flower coloring through metabolic engineering
- High accumulation of γ-linolenic acid and stearidonic acid in transgenic perilla seeds
- Production of recombinant Tissue-Type Plasminogen Activator (t-PA) protein in rice
- Shelf life extension of fruit and improvement in growth through sound wave treatment
-
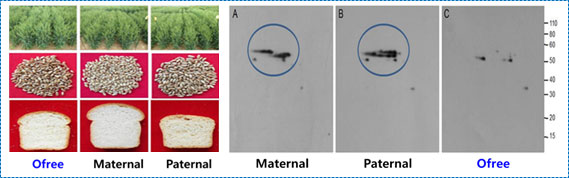 Allergy-reduced wheat "Ofree"
Allergy-reduced wheat "Ofree"
-
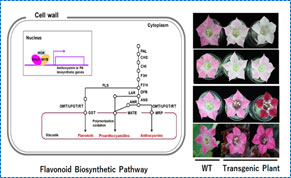 Flower color modification
Flower color modification
-
 Lipid biosynthesis modification
Lipid biosynthesis modification
-
 Production of t-PA in rice
Production of t-PA in rice
-
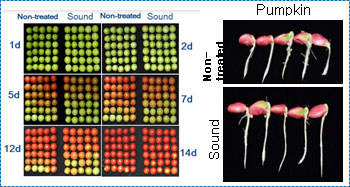 Effect of sound wave on fruit ripening and seed germination
Effect of sound wave on fruit ripening and seed germination
(3) Gene Engineering Division
Function
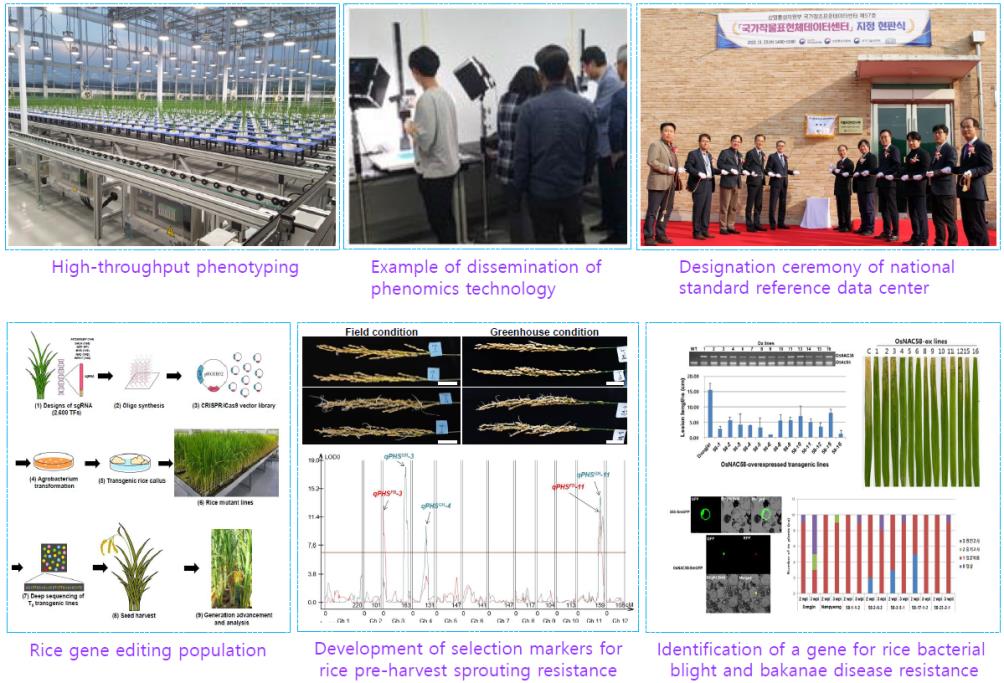
- Operation of the National Crop Phenomics Center and dissemination of phenomics technology
- Development of biotic and abiotic resistance breeding materials through genome editing
- Identification of useful genes and development of molecular markers for crop breeding
Major Achievements
- Establishment and application of crop phenotyping system based on plant phenomics
- Development of phenomics technology for measuring seed traits, growth, and drought tolerance
- Dissemination of phenomics technology through collaborations including the Eureka project - Designation of the National Crop Phenomics Center as a national standard reference data center by the Ministry of Trade, Industry, and Energy of Korea
- Establishment of a rice genome editing population and functional analysis
- Map-based cloning of useful genes and development of selection markers for crop breeding
- Rice pre-harvest sprouting resistance and bakanae disease resistance markers - Discovery of genes related to pathogen defense (e.g. rice bacterial blight resistance)
(4) Biosafety Division
Function
- Risk management for research handling GMOs
- Environmental risk & food safety assessment of GM crops
- Development of technology for GMO monitoring and traceability
- Risk assessment for new breeding technology (e.g. genome editing)
Major Achievements
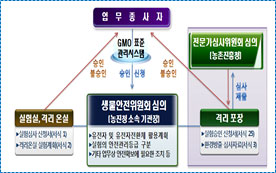
- Establishment & operation of the Institutional Biosafety Committee
- Management of experiments in confined research facilities (labs, green houses) & biologically isolated fields - Development of guidelines for environmental risk assessment of GM crops
- Drought-tolerant rice, nutrient-improved rice, insect-resistant rice, herbicide-tolerant grass, etc.
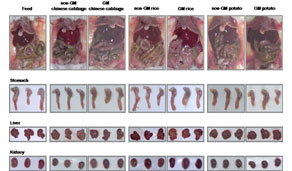
- Molecular characterization, evaluation of agronomic traits, and impacts on target & non-target organisms - Development of guidelines for food safety assessment of GM crops
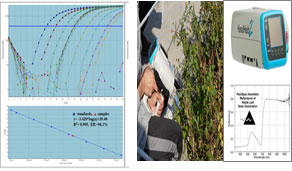
- Compositional analysis, toxicity, allergic potential, metabolic profiling, etc. - Development of detection techniques for GMO monitoring and traceability
- PCR method (qualitative & quantitative), spectroscopy (near-infrared), etc.
-
 Institutional Biosafety Committee
Institutional Biosafety Committee
-
 Green house
Green house
-
 Biologically isolated fields
Biologically isolated fields
-
 Environment risk assessment
Environment risk assessment
-
 Food safety assessment
Food safety assessment
-
 GMO detection
GMO detection