Research
Research
- Planning and Coordination Division
- General Services Division
- Technology Services Division
- Dept. of Agricultural Environment
- Dept. of Agricultural Biology
- Dept. of Agro-food Safety and Crop Protection
- Dept. of Agricultural Engineering
- Dept. of Agricultural Biotechnology
- National Agrobiodiversity Center
- Research Paper
Dept. of Agricultural Environment(농업환경부)
The Department of Agricultural Environment is a national research organization supporting rural areas to maintain sound agricultural environments through the development of rural resources and new agricultural technologies.
(1) The Department of Agricultural Environment focuses on:
- Managing the soil and nutrient levels of agricultural land and building up the system to make effective use of information on agriculture and the environment
- Utilizing climate resources, reducing greenhouse gas emissions, and improving agricultural ecosystem soundness
- Setting up a technology system for low-input, closed-loop, organic agricultural production
- Generating income from agricultural environment resources and establishing a foundation of welfare for rural communities
It consists of the Soil and Fertilizer Division, Climate Change Assessment Division, Organic Agriculture Division, and Rural Environment & Resources Division.
(2) Soil and Fertilizer Division
Contributes to the rational utilization of agricultural land and the improvement of rural household incomes by conducting research into farmland soil resources, establishing standards for physiochemical properties, developing optimum management techniques, managing crop nutrition, and advancing fertilizer resource application technologies.
1. Updating of soil resource information and expansion of soil information services
Updating soil information in line with changes in land use, conducting soil surveys on Saemangeum Agricultural and Ecological Land, making digital soil maps reflecting soil properties, collecting big data for soil security assessment, and performing studies on rapid soil survey techniques using proximal soil sensing.
-
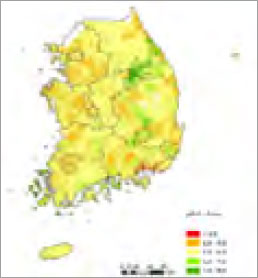 Standard layer of soil pH (0 - 5cm)
Standard layer of soil pH (0 - 5cm)
-
 Soil Judging Contest
Soil Judging Contest
-
 Agreement with farmland banking enterprise
Agreement with farmland banking enterprise
2. Development of water movement and management techniques and dissemination of current and predictive drought information
Setting standards on soil physics for agricultural land and developing land improvement technology, developing water management techniques for outdoor and greenhouse cultivation, providing current and predictive drought information, assesses soil loss, and developing soil conservation practices.
-
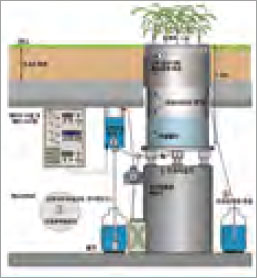 Water movement research using undisturbed weighing lysimeter
Water movement research using undisturbed weighing lysimeter
-
 Guideline for water management techniques on crop land
Guideline for water management techniques on crop land
-
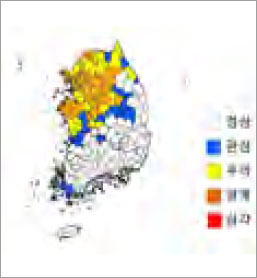 Services for drought status and prediction on uplands
Services for drought status and prediction on uplands
3. Evaluation of changes in agricultural environment resources, performance of soil tests, and development of on-site diagnosis and prescription techniques
Periodically monitoring and evaluating the chemical properties of national agricultural land, developing technologies to protect agricultural land from heavy metals, setting soil chemistry standards, supporting test-based policies for preserving agricultural environments, performing soil diagnoses, and prescribing productivity techniques for farming sites.
-
 Environment monitoring workshop
Environment monitoring workshop
-
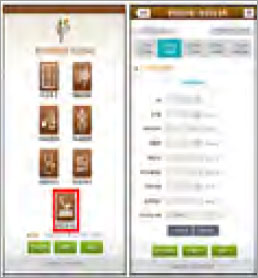 On-site diagnosis system for soil chemical management
On-site diagnosis system for soil chemical management
-
 On-site diagnosis contest
On-site diagnosis contest
4. Improvement of fertilizer application prescription services and support of agricultural environment preservation programs
Developing integrated nutrition management and assists in providing financial support to farmers by setting fertilizer recommendations, studying fertigation prescriptions, modeling nutrient transportation in agricultural land, calculating the nutrient balance of agricultural land to provide improvement measures, and performing nutritional diagnosis in accordance with crop growth stage.
-
 Publication of fertilization recommendation
Publication of fertilization recommendation
-
 Development of fertigation(irrigation+nutrients) recommendation
Development of fertigation(irrigation+nutrients) recommendation
-
 Farmhouse practice manual for conservation of agriculture and rural environments
Farmhouse practice manual for conservation of agriculture and rural environments
5. Development of techniques for safe use of organic matter in agricultural land and assessment of soil carbon changes
Developing technologies to utilize organic resources in agriculture and ensure safe use, setting the recommended amount of organic fertilizer to be applied, evaluating environmental changes to land caused by long-term use of fertilizer, and studying and predicting soil carbon changes to maintain the optimal amount of organic matter in agricultural land.
-
 Management of long-term field experiment ('54 -)
Management of long-term field experiment ('54 -)
-
 IoT compost maturity determination system
IoT compost maturity determination system
-
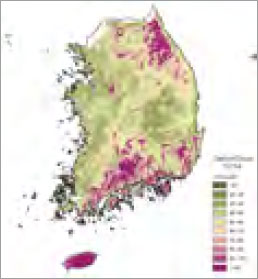 Assessment of soil carbon stock
Assessment of soil carbon stock
(3) Climate Change Assessment Division
Refines agrometeorological data and disaster-related information; anticipates the effect of climate change on agricultural ecosystems, assesses vulnerability, and advances primary crop yield forecasting information. Additionally calculates greenhouse gas emissions and fine dust and responds proactively to new climate regime issues by striving to develop greenhouse gas reduction technologies.
1. Refinement of the calculation of greenhouse gas emissions in the agricultural sector and development and practical use of reduction technologies
Analyzing greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions by establishing a National GHG Inventory in the agricultural sector and responding to global institutional (UNFCCC) efforts to improve climate change policies. Also contributing to the promotion of ‘net-zero’ through the development and application of GHG reduction technologies and carbon life cycle assessment.
-
 Development of Korea-specific emission factors
Development of Korea-specific emission factors
-
 Real-time greenhouse gas measuring device
Real-time greenhouse gas measuring device
-
 Rice field water management and greenhouse gas reduction
Rice field water management and greenhouse gas reduction
2. Evaluation of fine particulate matter emissions in the agricultural sector and assessment of atmospheric environmental impacts
Monitoring and conducting inventory of the emission characteristics of fine particulate matter in the agricultural sector, and also upgrading the calculation of fine particulate matter emissions. Additionally conducting the management of fine particulate matter and ammonia emission information and assessing the impact of the atmospheric environment on agricultural areas.
-
 Agricultural land ammonia emission calculation system
Agricultural land ammonia emission calculation system
-
 Assessment of atmospheric environmental impact
Assessment of atmospheric environmental impact
-
 Calculation of fine particulate matter emission
Calculation of fine particulate matter emission
3. Research on climate change at agroecosystem and assessment of climate change impact and vulnerability
This laboratory develops climate indices for evaluating the impact of climate change and assesses climate change effects and vulnerabilities on agricultural environment, biodiversity and biological seasons. It also develops technologies that can minimize the impact of climate change to maintain the function of agricultural ecosystem services.
-
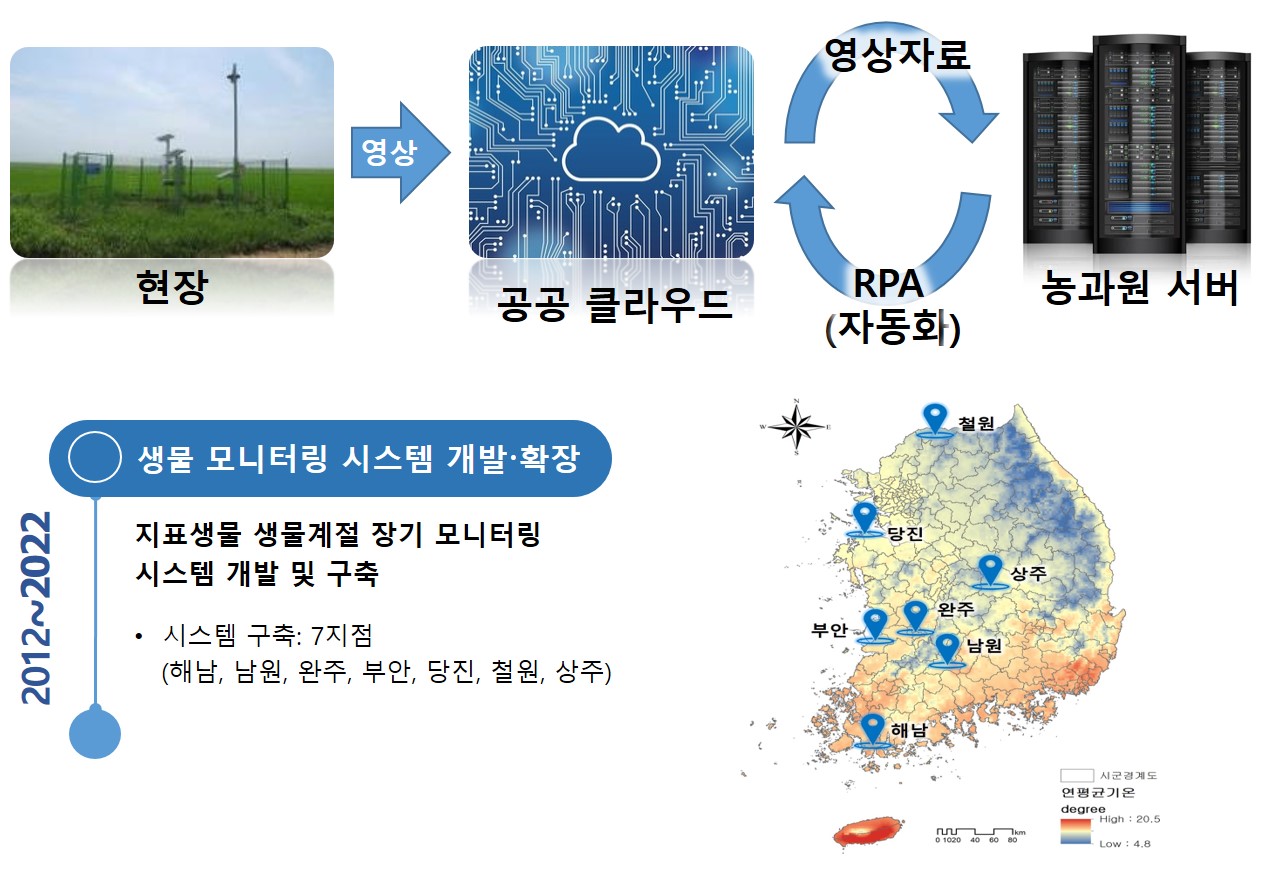 Real-time monitoring system for climate change indicator species in agroecosystem
Real-time monitoring system for climate change indicator species in agroecosystem
-
 Assessing climate change vulnerabilities on agricultural environment and agroecology
Assessing climate change vulnerabilities on agricultural environment and agroecology
-
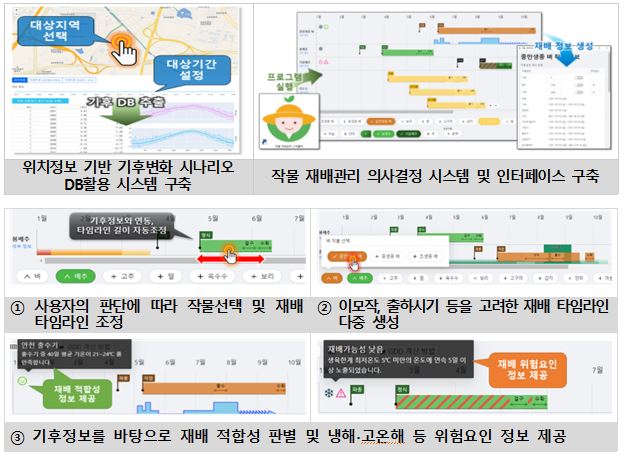 Development of climate change risk management technologies
Development of climate change risk management technologies
4. Production and prediction of agro-meteorological information for adaption to climate change
This laboratory advances the field-specific early warning service for weather risk management for small-scale farms, evaluates agro-climatic resources, and predicts agro-climatic variability on multiple timescales based on climate models for climate change adaptation in agriculture. Moreover, it builds an agro-meteorological big data, estimates farm-scale climate by using downscaling technologies (such as AI, geospatial climatology model), and assesses micro-meteorological fluxes (such as latent heat) in agricultural land.
-
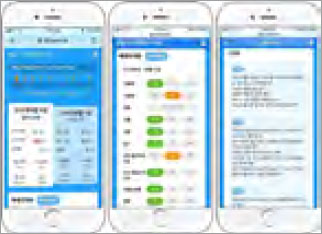 Early warning service for agrometeorological disasters
Early warning service for agrometeorological disasters
-
 Mid-and long-term agrometeorological and agro-climatic forecasts
Mid-and long-term agrometeorological and agro-climatic forecasts
-
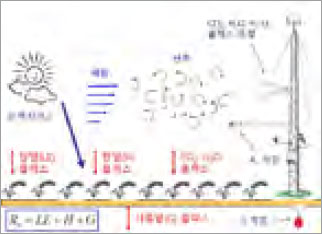 Agricultural land flux measurement system
Agricultural land flux measurement system
5. Measurement of agricultural production environments based on remote-sensing and advancement of crop yield forecast technology
Evaluating the yields of primary domestic and foreign crops based on remote sensing methods, as well as monitoring agricultural production environments. Also observing and analyzing agricultural disasters by utilizing remote sensing technologies and establishing a base to apply satellite images in the agricultural sector.
-
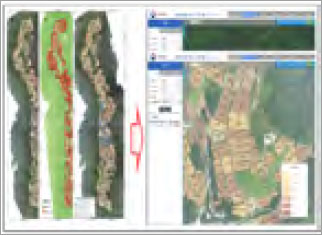 Unmanned observation information service platform
Unmanned observation information service platform
-
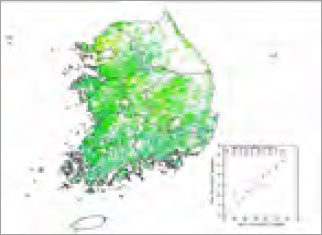 Remote-sensing-based crop yield forecast
Remote-sensing-based crop yield forecast
-
 Application of agricultural satellite
Application of agricultural satellite
(4) Organic Agriculture Division
We develop field-focused, low-input resource cycling technologies to resolve technical difficulties in organic farming and put them to practical use, thereby contributing to the development of eco-friendly organic farming.
1. Regenerative Organic Ecological Value Consumption Laboratory
The Regenerative Organic Ecological Value Consumer Laboratory conducts research on the establishment of an environmental and ecological value assessment system for organic farming and on ecological management technologies using natural enemies. Nationwide surveys are conducted to assess the biodiversity of agricultural lands, establishing a value assessment framework for the integrity and diversity of organic farming ecosystems. Furthermore, biological pest management techniques using companion plants and natural enemies are being developed. The practical application of these technologies is promoted through the establishment of a comprehensive ecological farming system and on-site verification of environmental ecosystem improvement. A K-regenerative organic farming model (Korea-regenerative organic farming model) that incorporates key technologies to enhance value consumption, soil health management, and animal welfare is being developed.
-
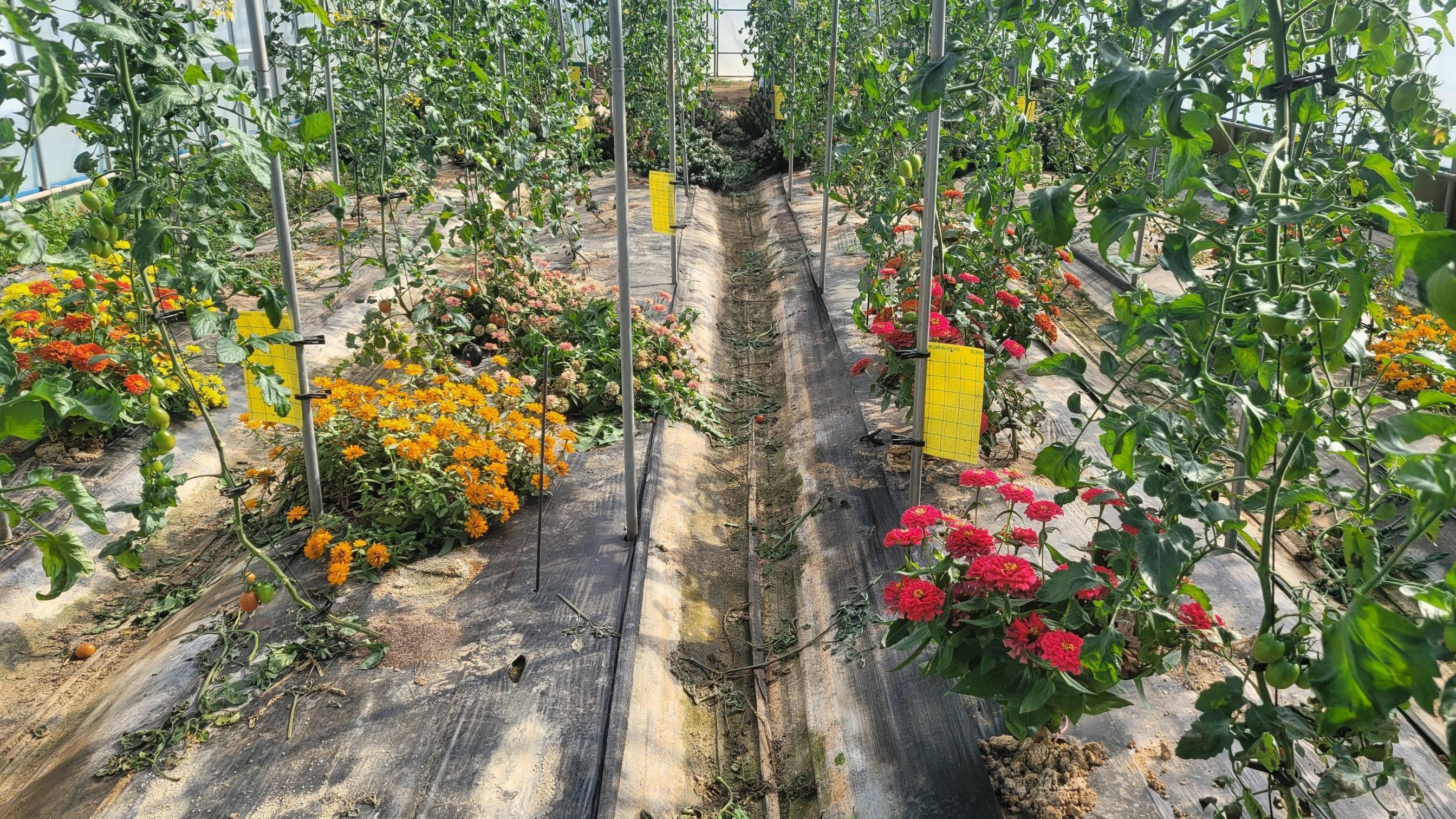 Development of pest management techniques using biodiversity-enhancing companion plants
Development of pest management techniques using biodiversity-enhancing companion plants
-
 Establishment of complex ecological agriculture to improve environmental ecology
Establishment of complex ecological agriculture to improve environmental ecology
-
 Development of a future-oriented regenerative organic farming model
Development of a future-oriented regenerative organic farming model
2. Regenerative Organic Soil Management Laboratory
The Regenerative Organic Soil Management Laboratory researches mitigation of and contributions to carbon neutrality in organic farming by comparing greenhouse gas emissions and developing technologies to reduce emissions. Furthermore, a fermented fertilizer production system has been developed by using domestic agricultural byproducts to localize and commercialize fertilizers and enhance their practical applicability. Data are collated on the characteristics of organic soil for different terrain types across the country to build data for soil health assessments. Research is being conducted to establish a soil quality assessment system and develop technologies to improve this system.
-
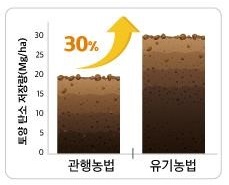 Research on the soil carbon storage in organic agriculture
Research on the soil carbon storage in organic agriculture
-
 Establishment of fermented fertilizer manufacturing technology using by-product resources
Establishment of fermented fertilizer manufacturing technology using by-product resources
-
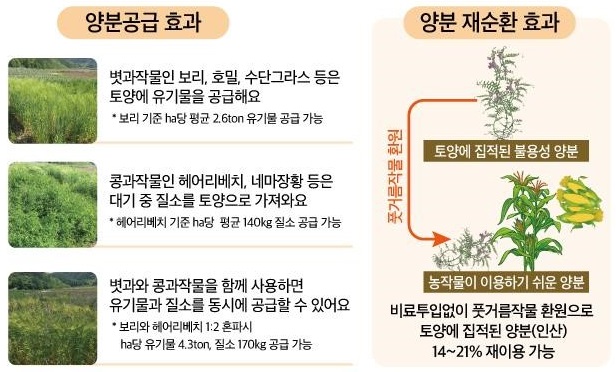 Determination of the effectiveness of soil nutrient supply using green manure crops
Determination of the effectiveness of soil nutrient supply using green manure crops
3. Regenerative Organic Farming Conversion Technology Laboratory
The Regenerative Organic Transformation Technology Laboratory conducts research on the transition to organic farming, focusing on the ecological value of agriculture and sustainable recycling. We explore methods to create a viable income model for organic farming at the farm level, including the development of essential organic conversion technologies specific to each crop. Various internal and external collaborative projects are being established to promote the value of organic farming and nurture young agricultural professionals. We conduct research on enhancing biodiversity and utilizing ecological resources in organic farming complexes using Regenerative organic agriculture conversion technology.
-
 Support for O.K.(Organic-Korea) Young Farmers to nurture young organic farmers
Support for O.K.(Organic-Korea) Young Farmers to nurture young organic farmers
-
 Promotion of organic garden contests to spread the values of organic farming
Promotion of organic garden contests to spread the values of organic farming
-
 Analysis and evaluation of the ecological resources of organic farming complexes
Analysis and evaluation of the ecological resources of organic farming complexes
4. Regenerative Organic Farming Conversion Technology Laboratory
The Regenerative Organic Cultivation Technology Laboratory aims to develop suitable agricultural techniques for organic farming cultural practices including organic seeds and seedlings and crop rotation, which are the foundation in regenerative organic agriculture. By integrating low-input and resource-cycling organic cultivation techniques with climate change-adaptive systems, this laboratory seeks to create a sustainable agricultural system and promote a healthy agricultural ecological environment. To establish organic farming cultivation techniques, existing nutrient managements and disease and insect pest control techniques are integrated. Models to enhance practicality and generate academic values through on-site research are being proposed. We also plan to publish organic cultivation manuals for major crops and disseminate them to agricultural fields, academia, and agricultural development agencies.
-
 Development of organic seeds and seedling production technology
Development of organic seeds and seedling production technology
-
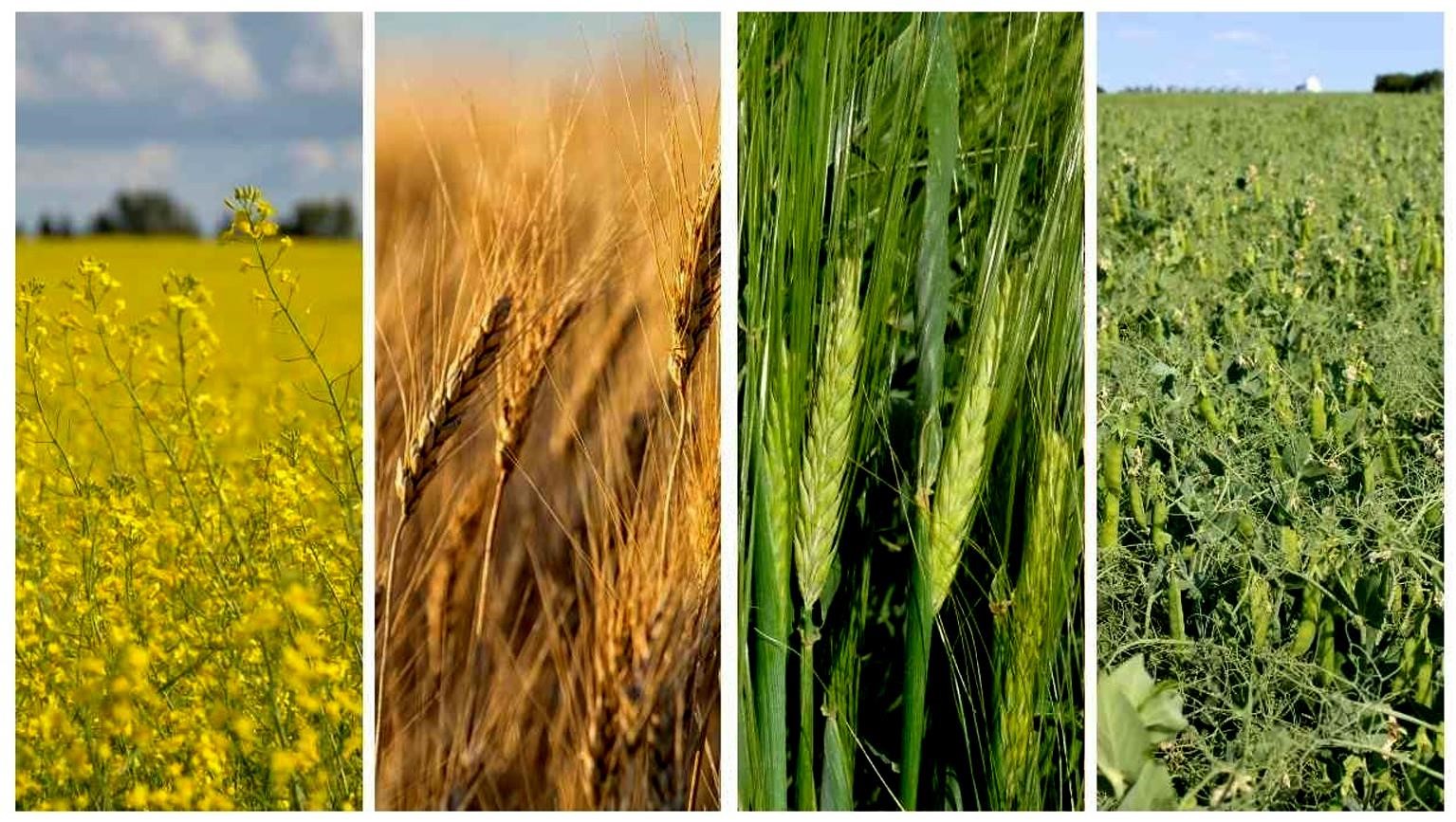 Research on organic cropping systems and cultivation technology
Research on organic cropping systems and cultivation technology
-
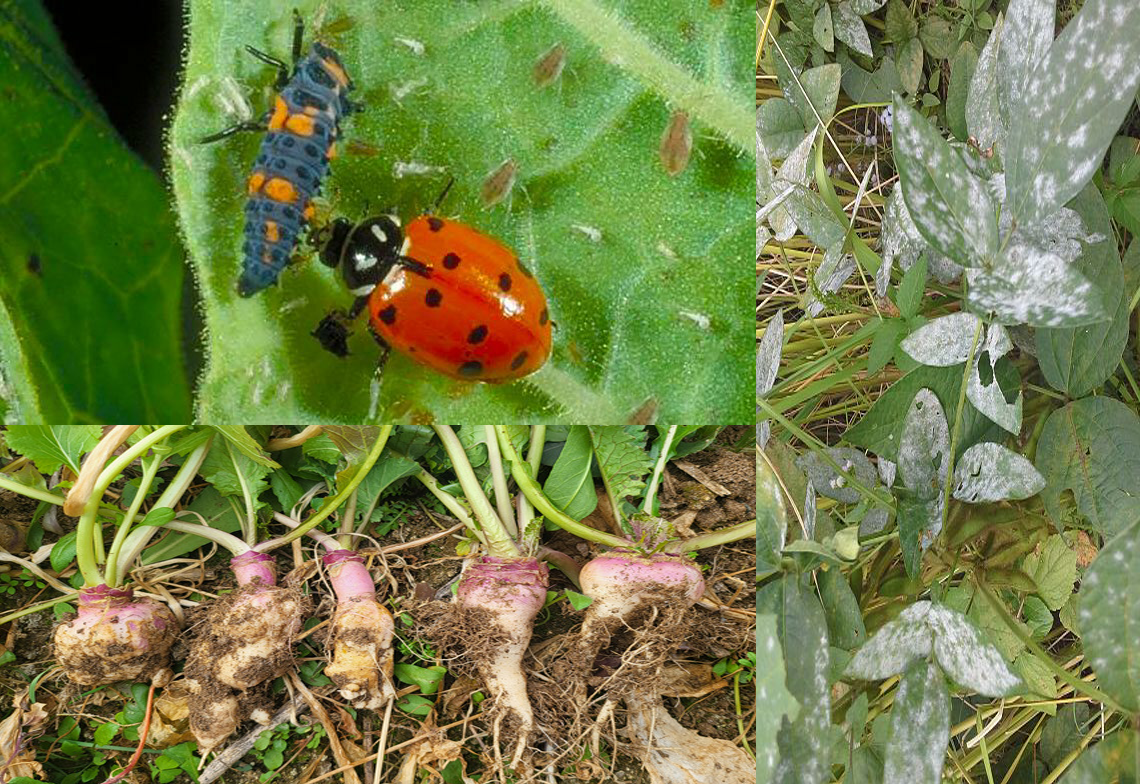 Research on the utilization of bioresources to improve crop health
Research on the utilization of bioresources to improve crop health
-
 Publication and dissemination of organic farming manuals
Publication and dissemination of organic farming manuals
(5) Rural Environment and Resources Division
The Rural Environment and Resources Division aims to contribute to the creation of rural areas where people want to go and live by improving the quality of rural residents’ life and enhancing the utilization value of agricultural and rural resources.
1. Supporting stable settlement of young and female farmers and enhancing the welfare of rural residents, including elderly farmers.
Conducting research into the welfare and capacity building of future agricultural human resources such as young farmers and female farmers. Also supporting tailored policy design through agriculture career system development and addressing the challenges posed by an aging rural population. Additionally offering social services to returning farmers to ensure their stable residency in rural areas.
-
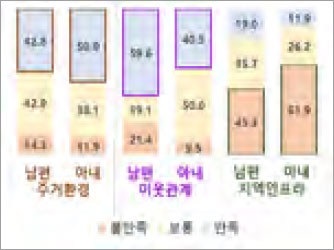 Satisfaction Chart of husbands and wives of farming households in rural Areas
Satisfaction Chart of husbands and wives of farming households in rural Areas
-
 Survey on Participation in Regional Agricultural Policy by Female Farmers
Survey on Participation in Regional Agricultural Policy by Female Farmers
-
 Women's Leadership Improvement Workshop for Married Immigrants
Women's Leadership Improvement Workshop for Married Immigrants
2. Rural spatial planning and regional regeneration research team
Striving to address the challenges of rural depopulation and to disseminate essential amenities into rural areas. Focusing on the development of rural space regeneration technologies to ensure the provision of basic amenities, create a conducive living environment, and preserve local resources including agricultural heritages and landscapes. Additionally actively involved in constructing spatial data, developing regional diagnostics and indicators, and setting planning standards that embody the essence of rural areas in support of the central and local governments' rural spatial planning policies. The goal is to propose innovative solutions for sustainable rural communities and to counteract rural decline through field-oriented community regeneration studies.
-
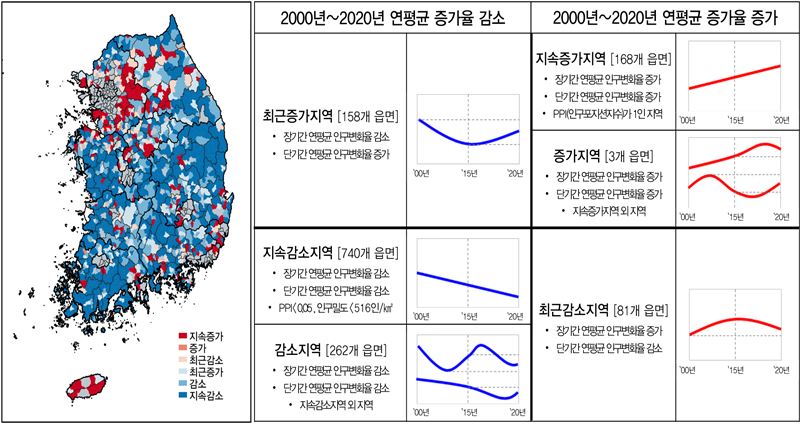 Rural typification by population change
Rural typification by population change
-
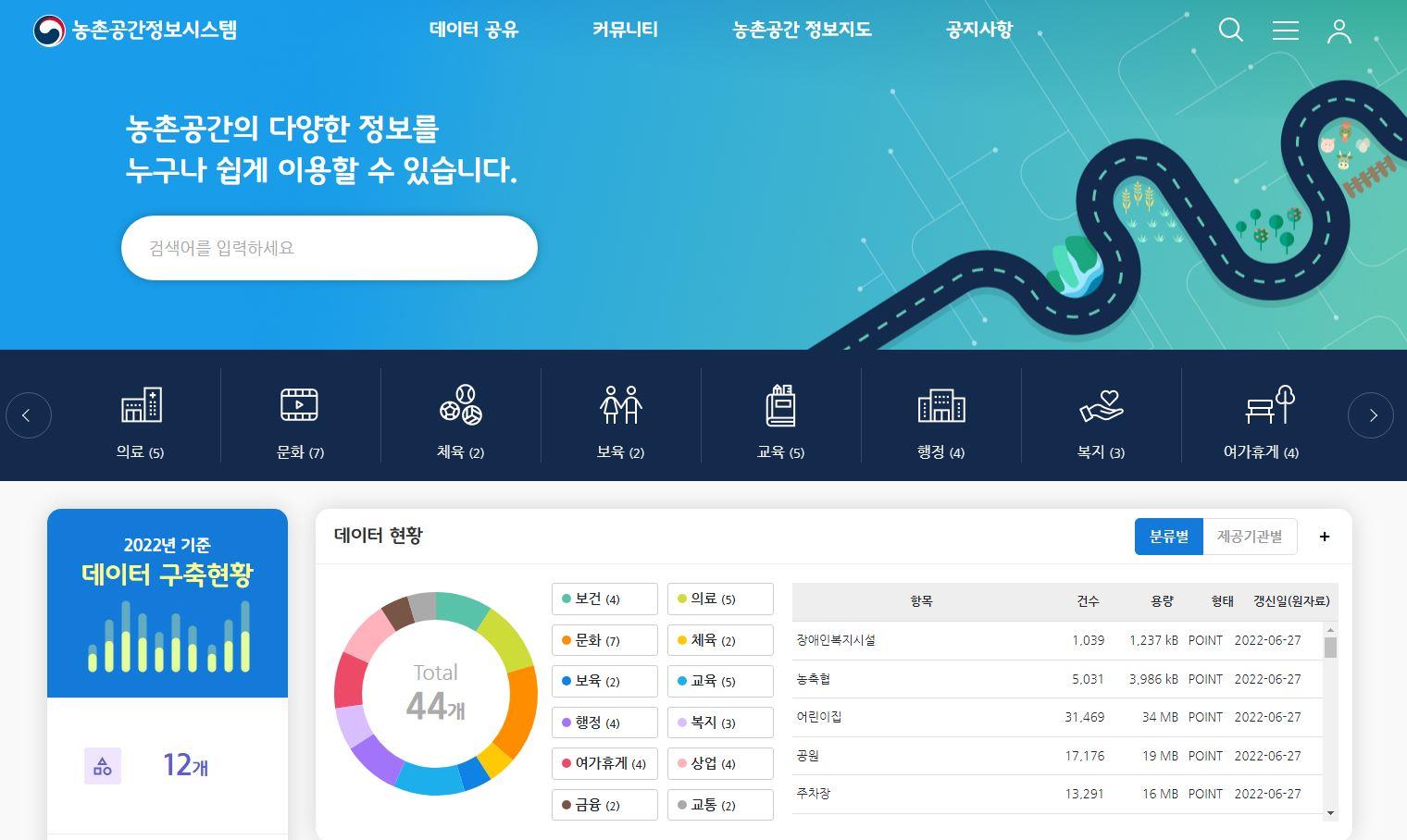 Rural spatial information system
Rural spatial information system
-
 The 4th Ruralism Forum
The 4th Ruralism Forum
3. Revitalization of rural healing tourism and improvement of rural tourism quality
Engaging in rigorous research to elucidate the inherent value of agricultural and rural landscapes as venues for rest and recreation. Such contributions are pivotal in augmenting the rural tourism market and establishing a competitive edge. This is accomplished through a multifaceted approach that encompasses the systematic exploration of regionally interconnected rural environments, the identification and cataloging of cultural assets, the development of specialized content in the realms of rural healing and ecotourism, as well as the strategic refinement of business practices and quality standards within the industry.
-
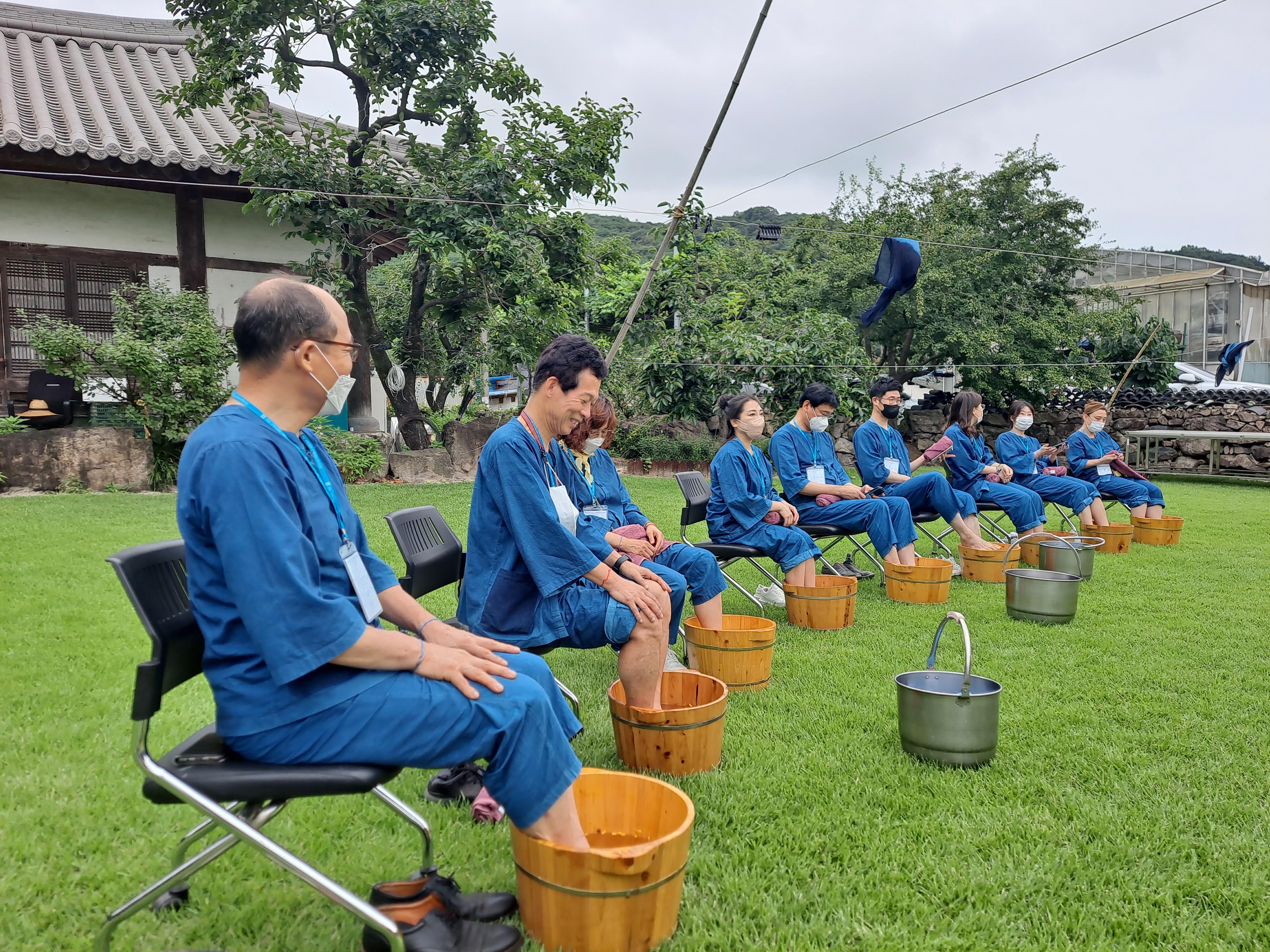 Development of Rural Healing Programs
Development of Rural Healing Programs
-
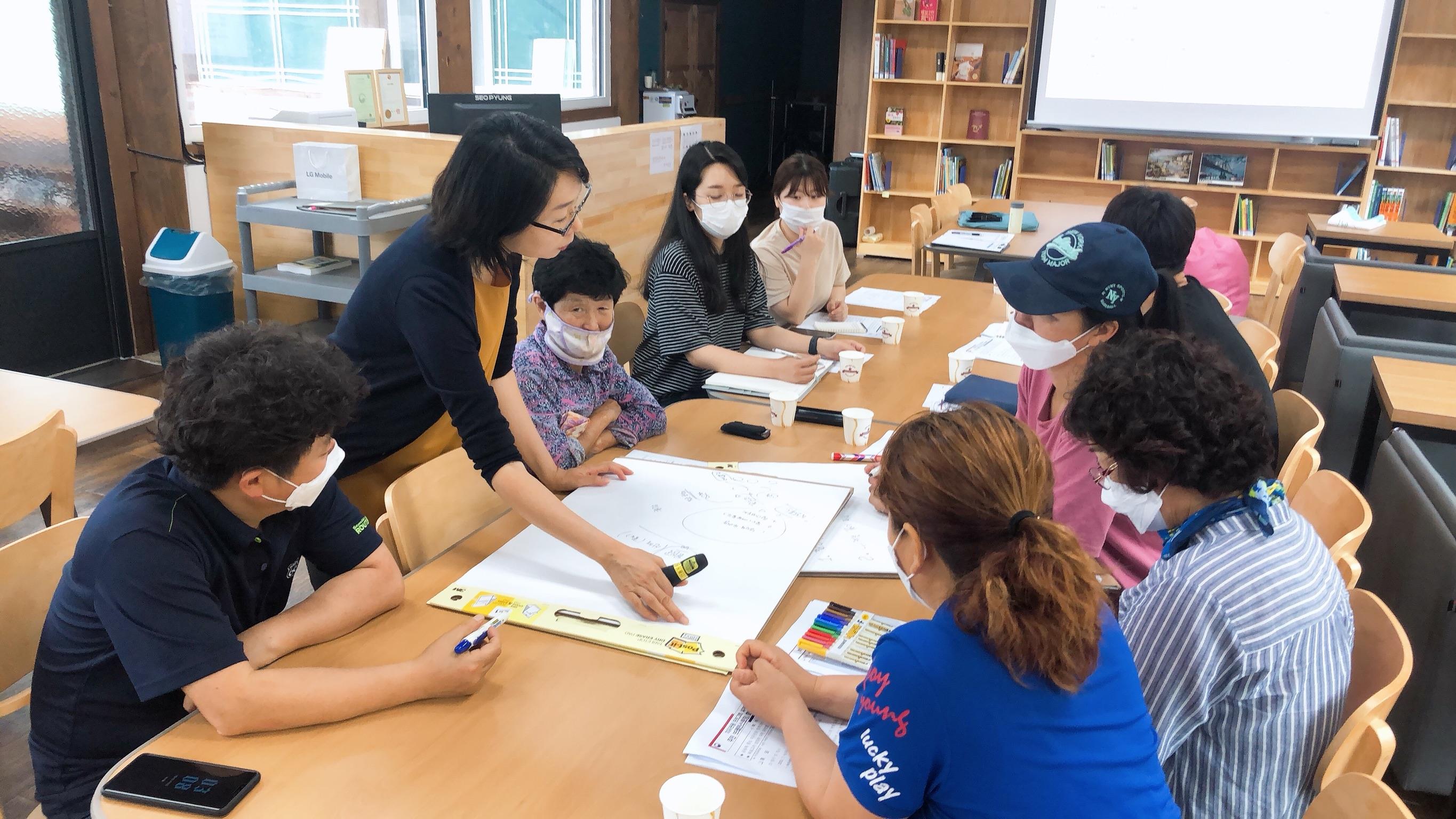 Exploration of Healing Resources through Community Brainstorming
Exploration of Healing Resources through Community Brainstorming
-
 A Fact-Finding Survey on Rural Tourism
A Fact-Finding Survey on Rural Tourism
4. Digitalization of rural resources to improve public value in rural areas
Conducting research into digitizing various rural resources and establishing a management structure to expand and enhance the value of functions that produce common benefits for agriculture and rural areas. Also contributing to creation of a social safety net and closing the gap between urban and rural areas through research on the well-being of rural residents.
-
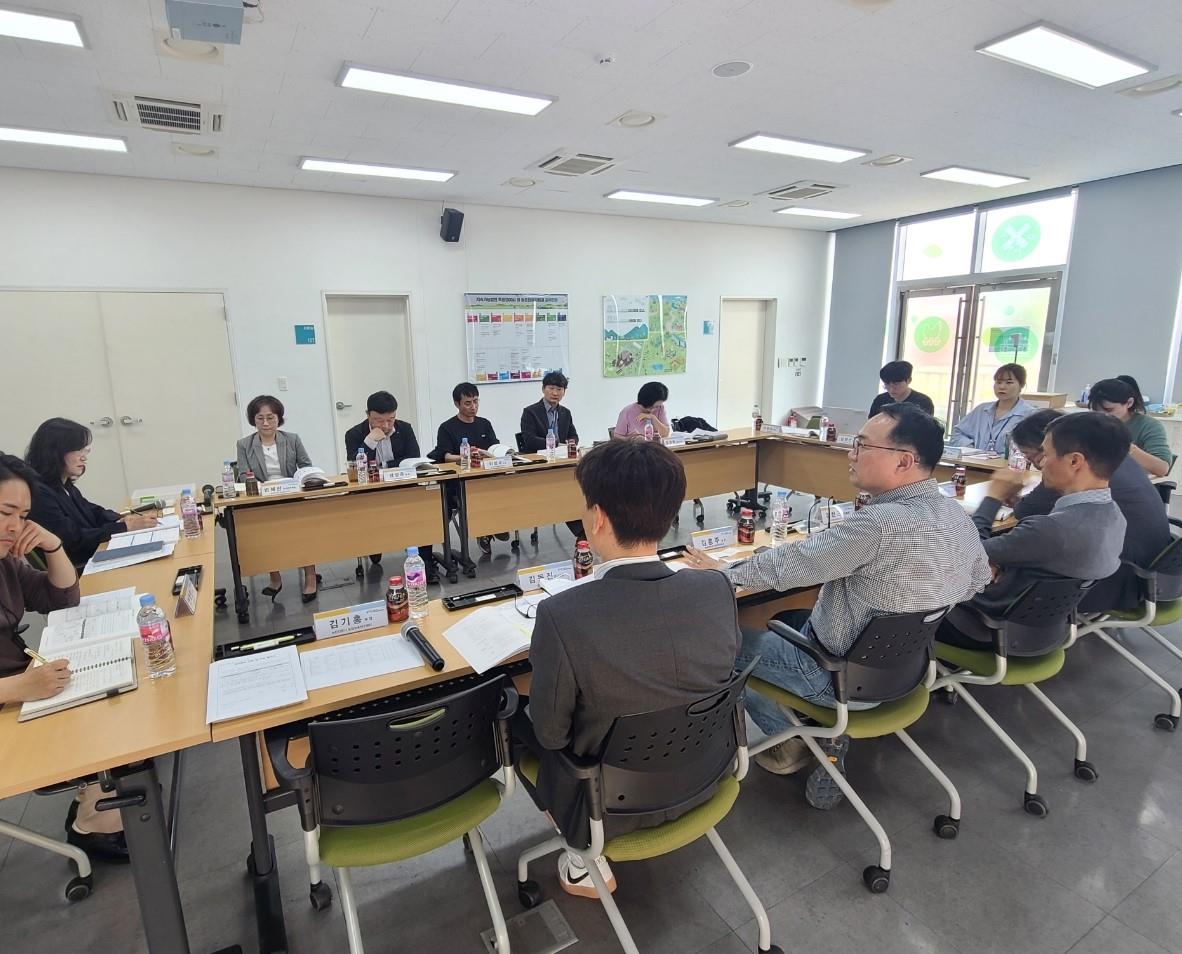 Expert Consultative Council on Rural Well-Being Survey
Expert Consultative Council on Rural Well-Being Survey
-
 Rural Well-Being Survey Report
Rural Well-Being Survey Report
-
 Digitizing Rural Resources by Drone
Digitizing Rural Resources by Drone